In today’s digital age, poor posture has become a common issue among childrens. The increasing use of technology, heavy school bags, and lack of physical activity all contribute to this growing problem. While poor posture might seem like a minor concern during childhood, it can have significant long-term effects on an individual’s health and well-being. This blog explores how poor posture in childhood can affect bone and muscle growth and the potential consequences in adulthood.
Understanding Posture
Posture refers to the alignment of the body parts in relation to each other at any given time. Good posture involves maintaining the natural curves of the spine, which are the cervical (neck), thoracic (upper back), and lumbar (lower back) curves. Poor posture, on the other hand, can lead to misalignment of these curves, resulting in various health issues.
The Growth Journey: Bones and Muscles
During childhood and adolescence, bones and muscles undergo significant growth and development. This period is crucial for establishing the foundation of a healthy musculoskeletal system.
Bone Growth
Bones grow in length and density during childhood. The growth plates, located at the ends of long bones, are areas of new bone growth. Proper alignment and posture are essential for even distribution of weight and pressure on these growth plates. Poor posture can lead to uneven pressure, potentially causing abnormal bone growth and alignment issues.
Muscle Development
Muscles provide support and stability to the skeletal system. During growth, muscles strengthen and adapt to the body’s changing structure. Poor posture can cause certain muscles to become overstressed while others weaken, leading to muscle power imbalances. These muscular imbalances can persist into adulthood, causing chronic pain and other joint issues.
Effects of Poor Posture on Bone Growth
Spinal Deformities
Conditions such as scoliosis (a sideways curvature of the spine) can develop or worsen due to poor posture. Scoliosis can lead to uneven growth of the vertebrae, causing a visible deformity and potential long-term complications.
Osteoporosis Risk
Poor posture can affect bone density. Children who do not develop strong, healthy bones due to poor posture and lack of physical activity may be at higher risk of developing osteoporosis later in life.
Joint Issues
Misaligned bones can place extra stress on joints, leading to conditions like osteoarthritis. Early wear and tear on joints can result in chronic pain and mobility issues.
Effects of Poor Posture on Muscle Growth
Muscle Imbalances
Poor posture often leads to overuse of certain muscles while others remain underused. This imbalance can cause pain, weakness, and limited range of motion.
Chronic Pain
Muscle imbalances and improper alignment can lead to chronic pain conditions, such as lower back pain, neck pain, and headaches. These issues can persist into adulthood, affecting quality of life.
Reduced Flexibility and Strength
Poor posture can limit the flexibility and strength of muscles. Children may grow up with reduced physical capabilities, impacting their ability to perform daily activities and increasing the risk of injuries.
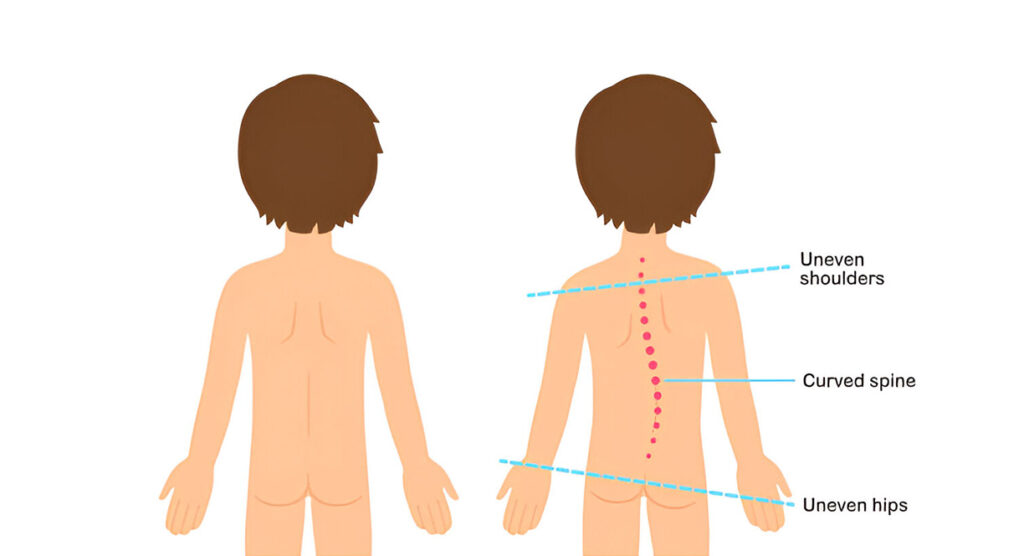
Long-Term Consequences in Adulthood
The effects of poor posture during childhood often extend into adulthood, leading to a range of health issues:
Chronic Pain
Persistent muscle imbalances and misaligned bones can cause chronic pain conditions that are difficult to treat.
Decreased Mobility
Long-term poor posture can lead to decreased flexibility and joint mobility, limiting an individual’s ability to perform everyday tasks.
Poor Physical Appearance
Visible signs of poor posture, such as rounded shoulders or a hunched back, can affect self-esteem and body image.
Breathing Problems
Poor posture can restrict the chest cavity, leading to shallow breathing and reduced lung capacity. This can affect overall health and physical performance.
Digestive Issues
Slouching can compress abdominal organs, potentially leading to digestive problems such as acid reflux and constipation.
Causes of Poor Posture in Children
Overuse of Technology
Prolonged use of smartphones, tablets, and computers encourages children to adopt slouched or hunched positions.
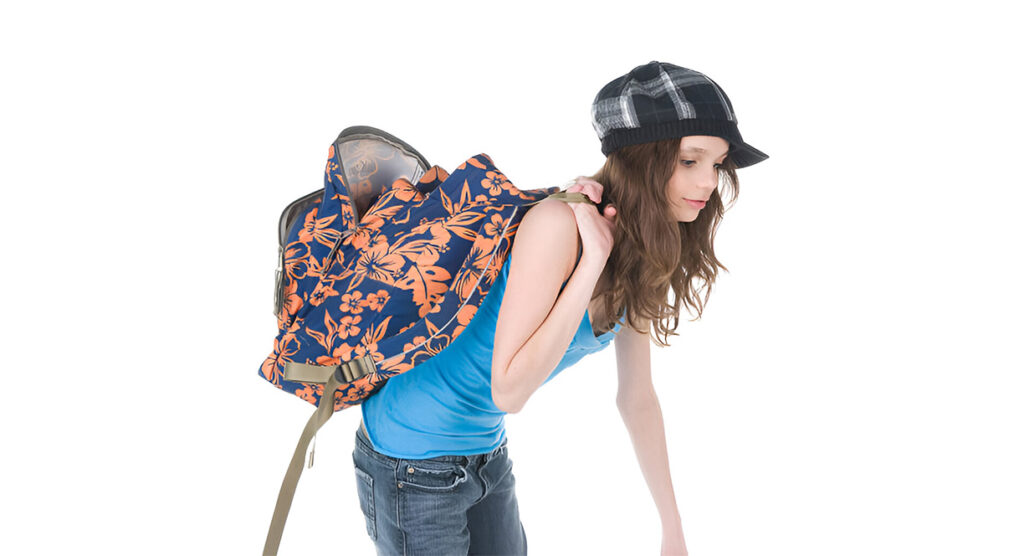
Heavy Backpacks
Carrying heavy school bags improperly can strain the spine and muscles.
Lack of Physical Activity
Sedentary lifestyles contribute to weak muscles, which are essential for maintaining good posture.
Emotional Factors
Stress and low self-esteem can also contribute to poor posture.

Prevention and Correction
Preventing and correcting poor posture in children is crucial for their long-term health. Here are some strategies:
Encourage Physical Activity
Regular exercise helps strengthen muscles and improve posture. Activities such as swimming, yoga, and dance are particularly beneficial.
Limit Screen Time
Encourage children to take breaks from screens and engage in physical activities that promote good posture.
Proper Ergonomics
Ensure that children use furniture that supports good posture, such as desks and chairs that are appropriately sized.
Educate About Posture
Teach children about the importance of good posture and how to maintain it.
Monitor Backpack Weight
Ensure that children carry backpacks correctly and that the weight is distributed evenly. The backpack should not exceed 10-15% of the child’s body weight.
Regular Check-Ups
Regular visits to a physiotherapist or pediatrician can help monitor and address any posture-related issues early on.
The Role of Physiotherapy in kids posture correction
Physiotherapy can significantly aid in posture correction for children by addressing muscle imbalances, improving strength, and enhancing flexibility. Through tailored exercises and activities, physiotherapists can help children develop proper postural habits, reduce discomfort, and prevent long-term musculoskeletal issues. Early intervention and regular physiotherapy sessions can ensure that children maintain a healthy posture, supporting their overall growth and development.
Conclusion
The impact of bad posture in childhood extends far beyond immediate discomfort. It can affect the growth and development of bones and muscles, leading to long-term health issues in adulthood. By understanding the causes and consequences of poor posture, parents and caregivers can take proactive steps to ensure children develop healthy posture habits. Encouraging physical activity, proper ergonomics, and educating children about posture are essential strategies for promoting lifelong health and well-being. Investing in good posture during childhood is an investment in a healthier, more active future.
Dr. Amit Saraswat
Senior Physiotherapist (Physioveda India)
20+ years of experience



Very good information
Poor posture in childhood can significantly impact bone and muscle growth, potentially leading to chronic issues in adulthood. As a physiotherapist, I’ve observed that improper posture can contribute to misalignments in the spine and pelvis, which may hinder optimal bone development and muscle strength. Addressing these issues early through corrective exercises and posture education can help mitigate long-term consequences and promote better overall musculoskeletal health.moreover, To improve a child’s posture, we must focus on a combination of exercises, ergonomic adjustments, and education. As well as, encourage activities that strengthen core muscles and improve flexibility, such as swimming or yoga. Ensuring proper ergonomic setup for studying and using electronic devices. Another approach should be Educating both the child and their caregivers about the importance of good posture and regular physical activity. Regular assessments and adjustments to the exercise program can also help address specific needs and prevent future issues. Inspite of that, to evaluate a child’s daily progress, monitor improvements through consistent observation and structured assessments can be done by tracking postural changes, pain levels, and range of motion. Using simple, age-appropriate exercises or activities to gauge physical improvements and adjust the program as needed. Regular feedback from the child and their caregivers about comfort and any difficulties can also provide valuable insights into their progress.