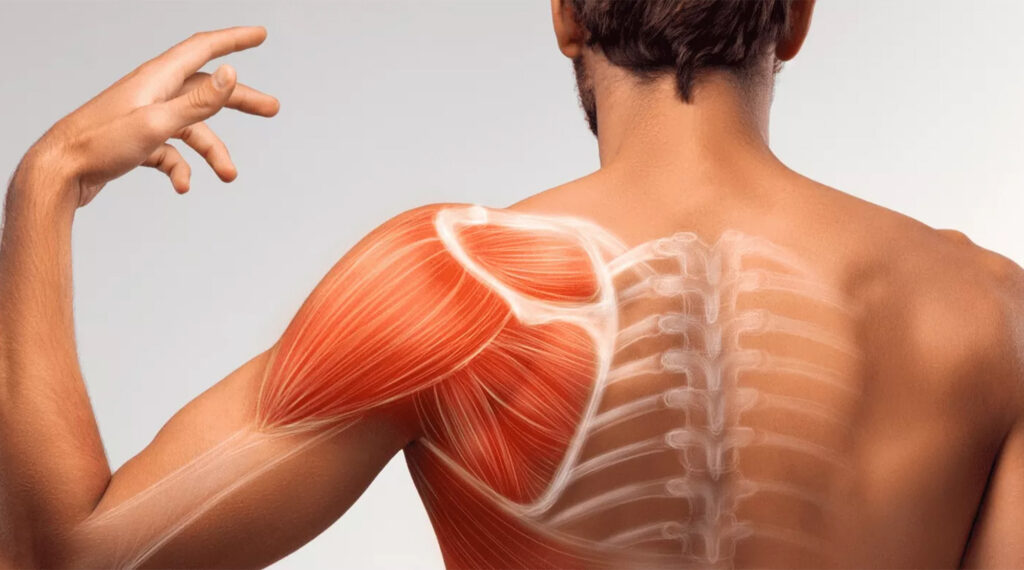
What is Muscle Imbalance?
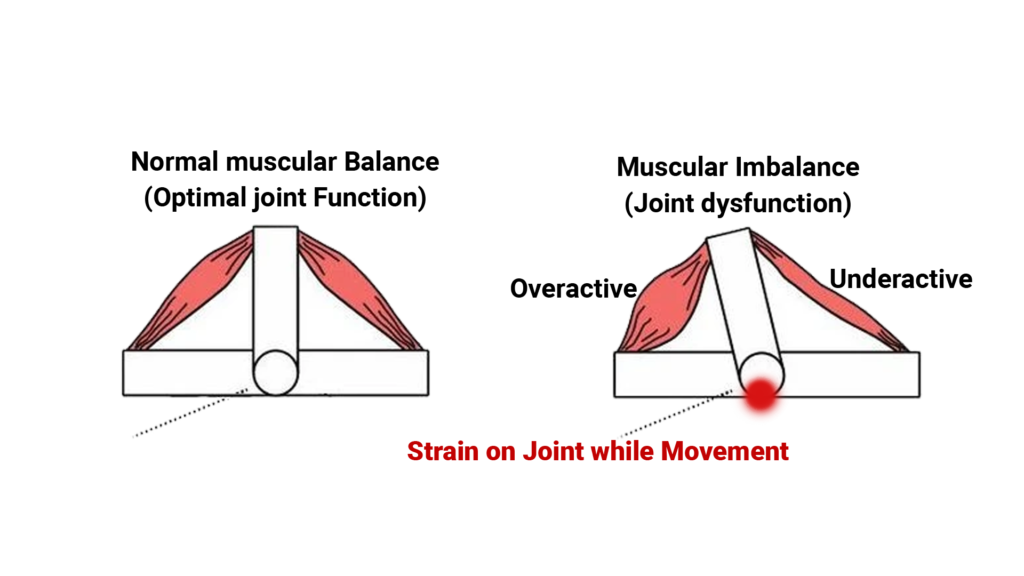
Muscle imbalance refers to a condition where the strength, length, and coordination of muscles are not evenly distributed throughout the body. This can occur when certain muscle groups are stronger or tighter than others, causing imbalances in the body’s structure and mechanics. As a result, this can lead to pain, limited range of motion, and increased risk of injury.
Muscle imbalances can develop due to a variety of reasons such as injury, overuse of certain muscle groups, poor posture, and inactivity. To correct muscle imbalances, it is important to identify the underlying cause and to engage in targeted exercises to strengthen weaker muscle groups and stretch tight muscles.
Physical therapy can also be helpful in addressing muscle imbalances. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program or treatment.
Role of physiotherapy in muscular imbalance
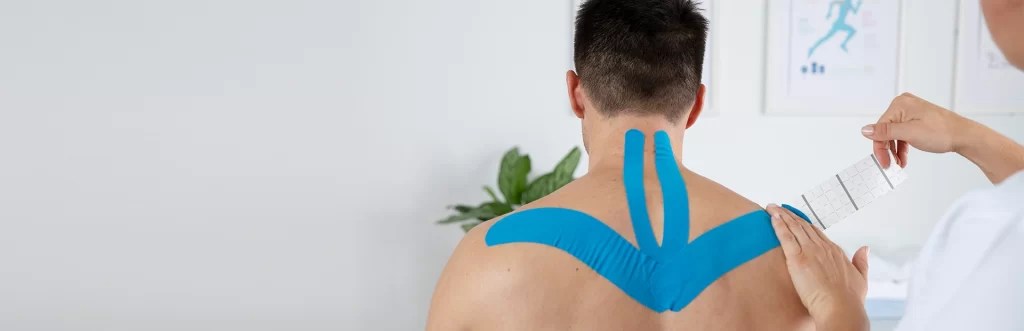
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in addressing and correcting muscle imbalances. Physiotherapists are trained to diagnose and treat a variety of musculoskeletal conditions, including muscle imbalances.
The following are some of the ways physiotherapy can help with muscle imbalances:
Assessment:
A physiotherapist will first perform a thorough assessment of the individual’s posture, movement patterns, and muscle strength to identify the underlying muscle imbalances.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises:
Based on the assessment, the physiotherapist will design a customized exercise program to address specific muscle imbalances. This may include stretching exercises for tight muscles and strengthening exercises for weak muscles.
Manual Therapy:
A physiotherapist may also use manual therapy techniques such as massage, joint mobilization, and trigger point release to improve muscle function and reduce pain.
Posture Correction:
The physiotherapist will also provide education on proper posture and body mechanics to help prevent the development of new muscle imbalances and promote overall musculoskeletal health.
Activity Modification
The physiotherapist may also provide advice on modifications to daily activities and work habits to help reduce the strain on specific muscle groups and promote healing.
Overall, physiotherapy can help individuals with muscle imbalances to reduce pain, improve range of motion, and restore normal movement patterns, leading to improved quality of life and reduced risk of injury.
Muscular Imbalances Cycle
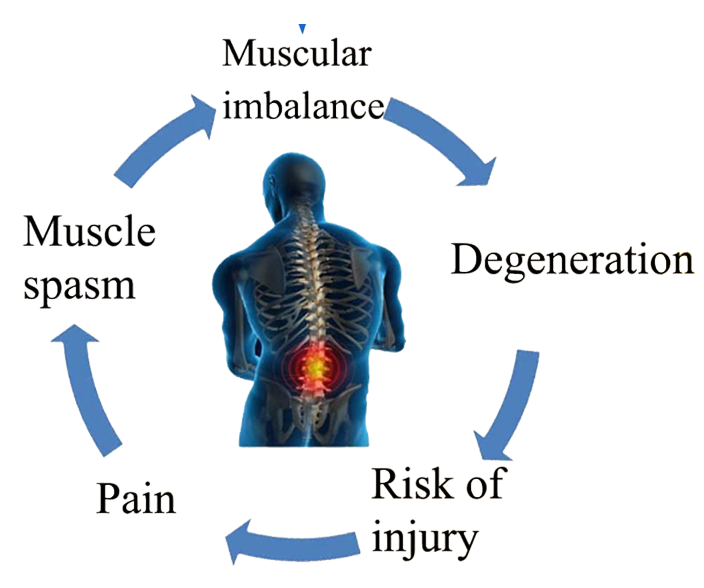
Muscular imbalances can have several negative consequences, including:

Pain
Muscle imbalances can lead to pain in the affected areas, as well as in other parts of the body due to improper alignment and compensation.
Increased Risk of Injury
Muscle imbalances can cause increased stress on certain joints and increase the risk of injury, particularly in high-impact activities such as running or jumping.
Limited Range of Motion
Tight muscles can limit range of motion and decrease flexibility, making it difficult to perform everyday activities and participate in physical activities.
Poor Posture
Muscle imbalances can also cause poor posture, which can lead to a variety of other musculoskeletal problems such as neck, back, and shoulder pain.
Reduced Physical Performance:
Muscle imbalances can also affect athletic performance by causing imbalances in force production and reducing efficiency in movements.
Decreased Quality of Life
The pain and limitations associated with muscle imbalances can reduce overall quality of life and limit one’s ability to participate in physical activities and hobbies.
It is important to address muscle imbalances as soon as they are identified to prevent further problems and to improve overall musculoskeletal health. Consulting a healthcare professional such as a physiotherapist can help individuals with muscle imbalances to develop a personalized treatment plan to address their specific needs.